

Scoliosis Spine Surgery Cost in India starts from US $9,000 and varies depending on the levels needed to be treated, medical history and comorbidities-if any, surgeon, hospital and the city where you choose to get the surgery done.
An important expense when it comes to your scoliosis surgery is going to be your spine surgeon's fees. IndiCure recommends only experienced, skilled, board-certified surgeons who are capable of delivering successful scoliosis surgeries. Although the charges may vary depending on the experience of the surgeon, you can be assured to be in safe hands with IndiCure.
A significant portion of the overall cost of the surgery arises from the use of any customized surgical instruments or specialized computer technology. With the hopes of improving patient care, new techniques and technologies are often introduced to the surgical process. Such innovative advancements in the surgical approach can increase costs.
Having your scoliosis operation in an accredited surgical facility by skilled and qualified medical staff is a critical factor. Moreover, the geographical location of this facility also affects the quote. But, IndiCure provides you with a projected estimate that will be all inclusive and affordable.
The surgery-related expenses include the pre- and post-surgical expenses. The pre-surgical expenses are associated with the age and medical condition of the patient and thus the number and type of investigations required. Post-surgical expenses may include prescription medications, physical therapy, and follow-up consultations.
We at IndiCure, understand that you travel with a budget in mind and do not like to be greeted by surprises after arrival in India. We thus club all these expenses and give you the package cost that is inclusive and affordable at the same time.
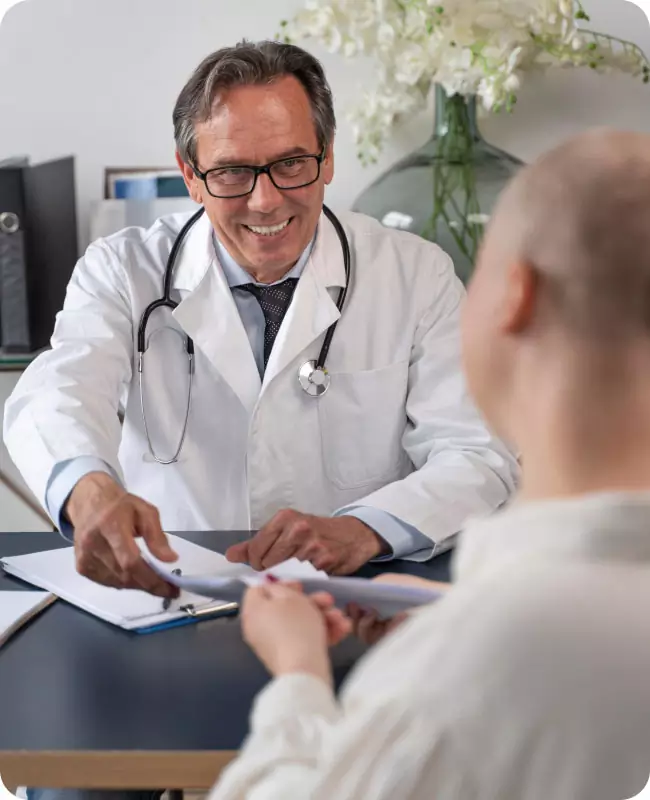
Your case manager shall give you an estimated cost of your surgery after discussing your medical reports with the surgeon. The final cost, however, shall be confirmed after your consultation with the Surgeon.
In fact, we have Special Negotiated Rates with the Hospitals and you can avail Discounted Rates when you choose to Travel with IndiCure.


We Help you Choose the Right Treatment, Surgeon & Hospital

We Arrange Video/Telephonic Consultation with the Surgeon

We Assist you with Visa & Accommodation

We Receive you at the Airport and Drop you at Hotel/Hospital
We Assist you the at Hospital & Provide Post Operative Support

New Delhi
BL Kapur Memorial Hospital is one of the biggest standalone private hospitals in Delhi, NCR. Established by late Dr. B L Kapur, an eminent Obstetrician, and Gynecologist on invitation by then Prime Minister of India, Mr. Jawahar Lal Nehru. The institute went on to become one of Delhi's premier multi-specialty hospitals.

Mumbai
Fortis Hospital, Mulund is a 300 bedded multispeciality tertiary care facility situated in the centre of the city, offering a range of clinical, diagnostic, and surgical services. The hospital began operations in 2002 and since then has achieved various milestones. The hospital is a JCI and NABH accredited facility and among very few hospitals to have NABH accreditation for Blood bank and NABL for Pathology Laboratory.
Scoliosis is the lateral curvature in a normal straight spine mostly occurring during the child's growing years. A side view shows convexity in upper back and concavity in lower back though it looks normal from front or back view. It can be seen in 3 shapes:
There can be many reasons for scoliosis, which can be categorized into:
Most cases of scoliosis are mild and do not require any surgery. However, some children develop deformities that continue to get severe as they grow, which can be disabling. Severe spinal curves can reduce the amount of space within the chest making lung functioning difficult.
The aim of the scoliosis surgery is threefold:
This is done by two methods
Once the bone fuses, the spine does not move and the curve does not progress.
The surgery is done by two approaches:
Posterior (done through back) or Anterior (through sides) approach. Both have their own merits and demerits.
The surgery for treatment of scoliosis in India is done under general anesthesia and can take anywhere between 4-12 hours depending on the curve and how much the spine needs to be fused. Hospital stay of about a week is required after the surgery to make sure you are on the right healing path.
Candidates for scoliosis spine surgery are adolescents if their curves are greater than 40 degrees and it continues to progress and adults with curves greater than 50 degrees. A good candidate for scoliosis spine surgery is one who is otherwise healthy, mentally and emotionally stable and can tolerate the surgery well.
We at IndiCure completely understand your concerns and it is always our endeavor to provide the best outcome for every patient. Following is the list of questions you must ask before you embark on your journey for scoliosis spine surgery in India.
Prepare to answer questions about your:

Severe deformation and rigid curvature requires another prior procedure called anterior release of disc space, after which bone is added to aid in fusion.
Curves present at thoracolumbar junction (T12-L1) can be treated by anterior approach.
Advantages of anterior approach are:
Scoliosis spine surgery is quite successful in stopping the curve from growing. With sophisticated techniques, doctors can straighten the curve to a great extent which improves the patient's appearance and functioning to a great extent.
You would have a lot of pain after the surgery which would be controlled with pain medications. You would stay at the hospital for about a week to ten days to make sure you are on the right healing path. The surgeon would advise you to start walking on the second or third day of the surgery and physical therapy would begin on the third or fourth day of the surgery.
Most people return to school and work in 3-4 weeks. Full recovery can take from 4-6 months and most people can resume other activities and even sports after advice from the surgeon.
More than 80% of the scoliosis are idiopathic, which means the reason for the curve is unknown. Scoliosis can also occur as a result of the degeneration of the spinal discs, which can happen as a result of osteoporosis, arthritis, or a hereditary disorder that frequently runs in families.
Scoliosis curves are measured by health professionals in degrees: Less than 20 degrees represents a minor curvature. Between 25 and 40 degrees is a moderate curve. Over 50 degrees is considered a steep curve.
The best long-term benefits are seen in scoliosis patients between the ages of 3 and 10 years.
It's never too late to undergo scoliosis surgery if you have scoliosis and are an adult.
Yes, scoliosis spine surgery is a major surgery. But the operation itself is just one stage of a drawn-out procedure.
Depending on the magnitude of the patient's curvature and how much of the spine needs to be fused, most fusions take 4 to 8 hours. A portion of this time is spent getting the patient ready for anesthesia, connecting them to various monitors, and arranging them for maximum safety and comfort.
Recovery from scoliosis surgery takes a while; patients usually need three to six months before they can resume their regular activities.
Any sort of spine surgery, including spinal fusion for the treatment of scoliosis, has the risk of complications, including infections, nerve damage, blood loss, and bowel and bladder issues.
The rods are typically placed for the rest of the patient's life. Approximately 2% of individuals have their rods removed. The most usual reason for rod removal is discomfort brought on by rods stinging nearby muscles.
The growth of the curvature is successfully stopped via spinal fusion. The curve can now be greatly straightened by doctors, which enhances the patient's attractiveness.
Your surgeon will only straighten your spinal bones as much as is necessary to safeguard your spinal cord.
How flexible your scoliosis is before surgery determines the extent of the correction. In general, the better the surgical correction, the more flexible your curvature is. Prior to surgery, your doctor might assess your flexibility using specialised X-rays known as bending or traction films. After surgery, the majority of patients have curves that are less than 25 degrees straightened. These little bends are frequently hardly perceptible.
There will be more pain than usual just after surgery, but this usually passes within a few weeks to months. Most patients claim that one year following surgery, their back pain is less severe than it was before.
Any restrictions you have following surgery will be explained by your surgeon. For the first six weeks, most patients will be instructed to avoid heavy lifting and limit their forward bending.
No, the majority of patients are able to resume all of their preferred pastimes and sports. Within 4 to 6 months of surgery, the majority of patients resume non-contact athletic activity (running, weightlifting, workouts).
All physical activity, especially contact sports, must wait until the spine has fully recovered. To get a strong spine fusion following surgery and resume your normal activities, it usually takes 6 to 12 months.
Enhance your medical journey to India by availing these extra services.
Traveling abroad for medical reasons may be challenging. With our experience of over a decade and working with the best surgeons and top hospitals in India, we help make your medical tour easier and safer for you. We will guide you at every step of the way and make end-to-end arrangements for your surgery, travel, and stay.
Ramandeep Dhaliwal
a month ago
I had great experience having rhinoplasty through Indicure. Dr. Ruchika from Indicure has helped me in finding best plastic surgeon, answering all my questions...
Read More
Joshua Archer
3 months ago
My name is Joshua Archer I'm from New Zealand, bay of plenty, kawerau I opted for the bypass surgery in January 2023 but planned it in advance for 28 September found IndiCure...
Read More
Kera Ren
8 months ago
Absolutely loved my experience with IndiCure - from first inquiring to meeting the surgeon pre op to my follow up post op. The surgeon was extremely approachable...
Read More
Andreana Paul
5 months ago
Had a wonderful experience. Visited India for my plastic surgery. From sending mails, airport pickup, comfortable accommodation and, to smooth hospital appointment booking...
Read More
Brandi Luce
5 months ago
I had the privilege of using Indicure's services for a cosmetic procedure that I had wanted for a long time but had always been apprehensive about. Ruchika helped me...
Read More
Jade M
3 years ago
Indicure Health Tours went above and beyond my expectations. They helped me with every aspect of my journey and were professional, kind and caring. I was...
Read More
The content on the website (www.indicure.com) is intended to be general information and is provided only as a service. All photographs on our website of before and after results are examples only, and do not constitute an implied or any other kind of certainty for the result of surgery.
Learn about IndiCure Health Tours' comprehensive editorial policy that strives to deliver trustworthy, helpful, relevant, accurate and people-first content on medical tourism in India.
It is not medical advice and should not be taken as medical advice. It should not be used to diagnose or treat a health condition and is in no way meant to be a substitute for professional medical care. You are advised to see a surgeon in person to assess what surgery may or may not accomplish for you.
It is also important to keep your expectations realistic and to understand that all surgical procedures carry risks and should never be taken lightly.